 We depend on our hands for just about everything, from grasping a toothbrush to typing on a keyboard. Bones, joints, connective tissues, and nerves make up the human hands, allowing for nimble movements. However, the structures that make up the hands are more delicate than other parts of the body, making them more prone to injury. You might experience hand pain for several reasons, including a harmless cut across your palm or a more severe injury like a broken bone. One other common reason for hand pain is arthritis. Arthritis of the hand can cause pain, stiffness, and swelling in your finger joints, impacting your ability to complete small, everyday tasks. But how do you know the difference between arthritis and something else? Here are the common causes of hand pain, including the different types of arthritis and their common symptoms.
We depend on our hands for just about everything, from grasping a toothbrush to typing on a keyboard. Bones, joints, connective tissues, and nerves make up the human hands, allowing for nimble movements. However, the structures that make up the hands are more delicate than other parts of the body, making them more prone to injury. You might experience hand pain for several reasons, including a harmless cut across your palm or a more severe injury like a broken bone. One other common reason for hand pain is arthritis. Arthritis of the hand can cause pain, stiffness, and swelling in your finger joints, impacting your ability to complete small, everyday tasks. But how do you know the difference between arthritis and something else? Here are the common causes of hand pain, including the different types of arthritis and their common symptoms.
Common Causes of Hand Pain
The location and severity of your pain can help determine what is causing your hand pain. Here are examples of common causes of hand pain and what types of symptoms you may experience.
Arthritis
Arthritis is the most common cause of hand pain. Arthritis typically occurs around the knuckles and joints in the fingers. Each joint has cartilage to help keep movements smooth and prevent bones from rubbing against one another. Arthritis will cause the cartilage or lining of the joints to deteriorate, which exposes the ends of your bones. This will lead to pain, swelling, stiffness, and even visible deformity of your joints and fingers. Arthritis is a progressive condition, which means when left untreated, it can cause these symptoms to get worse. Everyday tasks like buttoning your shirt or tying your shoe can become difficult due to hand arthritis.
Nerve Damage
When nerves in and around the hand become damaged, you may develop pain, numbness, and weakness in your hands. One example of nerve damage is peripheral neuropathy, which can affect the nerves in your hands and wrists that control sensations and muscle movement. With nerve damage or peripheral neuropathy, you may notice a prickling or tingling sensation in your hands that may develop gradually. Peripheral neuropathy can also lead to sharp, burning pain that radiates from your wrist into the tips of your fingers. Nerve damage in the hands can lead to a lack of coordination and muscle weakness.
Sprains & Fractures
A sudden injury can lead to a sprain or fracture, which will cause pain at the injury site. Hand injuries are common in falls or while playing sports. Certain occupations, like construction, can put your hands at greater risk for injury. A fracture refers to a broken bone in the hand, while a sprain will typically impact muscles in the hand. You can also suffer a sprained or fractured wrist, which can cause pain and discomfort when you move your hand. Because the structures in the hands are so delicate, getting treatment right away for any hand injury is important to avoid permanent damage to your hand and dexterity.
Overuse Injuries
An overuse injury can occur when you engage in repetitive movements that put additional stress on the structures in your hand. For example, repetitive hand and wrist movements can cause inflammation in and around the median nerve, which controls your finger movement. This type of overuse injury is known as carpal tunnel syndrome and can cause burning or tingling sensations in the palm of your hand. Carpal tunnel syndrome can also cause tingling and numbness in your thumb, index finger, and middle finger.
Chronic Health Conditions
Chronic health conditions can also lead to hand pain or worsen it. One such health condition is known as De Quervain’s tenosynovitis, which causes swelling in the tendons around your thumb. It can cause pain and make it difficult to grasp or pinch objects. Raynaud’s disease is another health condition that can cause your extremities like hands and feet to become cold and change colors. Raynaud’s disease can lead to a pins and needles sensation in your fingertips.
Types of Hand Arthritis
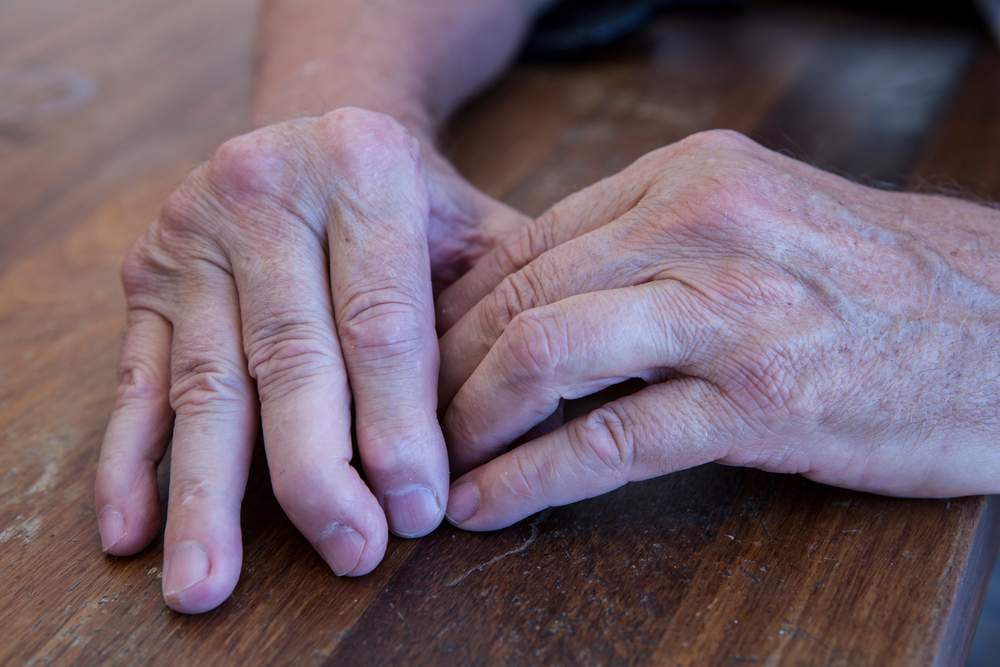 In order to distinguish hand pain from arthritis of the hand, it helps to get a better understanding of the main types of hand arthritis that can affect you. Here are four types of hand arthritis, their causes, and distinguishing symptoms.
In order to distinguish hand pain from arthritis of the hand, it helps to get a better understanding of the main types of hand arthritis that can affect you. Here are four types of hand arthritis, their causes, and distinguishing symptoms.
Osteoarthritis
General wear and tear on the joints can lead to osteoarthritis, which is the most common form of arthritis. Many people develop osteoarthritis later in life as the cartilage that cushions and covers the joints starts to wear down over time. Osteoarthritis of the hand can cause pain when the ends of bones rub together in the joints of your fingers and hand. The most common places for osteoarthritis in your hands are in the wrist, the base of your thumbs, and the top joints of your fingers. Osteoarthritis of the hand can also cause stiffness and result in a loss of mobility over time.
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis is an inflammatory disease where the body’s immune system attacks its own tissues, causing the lining of the joints to swell. The joints depend on a lubricant known as synovium to allow cartilage to easily glide against one another. As inflammation develops in the area because of the immune response, the cartilage and bones can start to erode over time. This can lead to the joints losing their shape and function. Rheumatoid arthritis typically affects joints on both sides of the body, so you are more likely to experience pain, swelling, and stiffness in the joints of both hands.
Psoriatic Arthritis
Psoriatic arthritis causes swelling and stiffness in the fingers and a skin condition called psoriasis. People who have psoriasis can develop psoriatic arthritis, which can come in waves and cause symptoms for a while before bouts of relief. Psoriatic arthritis most commonly affects a few fingers at a time and leads to obvious swelling, joint pain, and stiffness in the morning or after long periods of disuse.
Post-Traumatic Arthritis
After an injury to your hand or wrist, you may develop what is known as post-traumatic arthritis. If you experience a sudden trauma, like a fracture or sprain, your body may trigger an immune response to the area that causes inflammation. Post-traumatic arthritis is generally temporary and will resolve with time, unlike arthritis caused by wear and tear.
Diagnosing Hand Pain
Talk to your doctor if you experience new or worsening hand pain. Some causes of hand pain, like osteoarthritis or an injury from repetitive movement, can cause symptoms that gradually worsen. A traumatic injury like a fracture will typically cause more sudden and immediate pain. Hand pain that occurs specifically around the joints, like your knuckles, the joints at the tips of your fingers, and the base of your thumb, are more likely associated with arthritis. Tell your doctor what symptoms you have been experiencing and if any movements or activities worsen the pain. Your doctor can diagnose arthritis or another cause of hand pain with a thorough physical examination and diagnostic imaging tools like an X-ray or bone scan. An X-ray will provide your doctor with highly detailed images of the bones in your hands, which can help identify areas of worn-down cartilage. Arthritis of the hand can also lead to the development of bone spurs, which are typically detectable on an X-ray. If your doctor suspects rheumatoid arthritis, they may recommend a blood test to confirm this diagnosis.
How to Get Lasting Relief for Hand Pain
Once your doctor has determined the cause of your hand pain, they can develop a personalized treatment plan to resolve it. Check out these strategies to relieve hand pain at home alongside treatments with your doctor.
Home Remedies
Applying cold and heat can help reduce swelling and soothe stiff joints. A cold compress will help restrict blood flow and slow the progress of swelling and inflammation in the area. A warm compress allows the soft tissues that support your hands and fingers to relax, which reduces stiffness. You can also take over-the-counter pain medication to address pain and inflammation for occasional or short-term relief.
Joint Stabilization
Your doctor may recommend a splint or brace to help stabilize the joints in your hand and wrist after an injury or while you heal. Joint stabilization with a splint or brace will also help you avoid further injury during the healing process. A splint or brace can also lessen the strain on the joint and help keep the joints properly aligned.
Stretches & Exercises
A physical therapist can also walk you through stretches and exercises to improve your mobility and functioning. Arthritis can negatively impact the range of motion in the joints, and learning how to improve strength and mobility in your hands and wrists can help slow the progression and reduce your discomfort.
Visit AICA Orthopedics in Marietta to learn more about what is causing your hand pain and how our team of doctors can help!