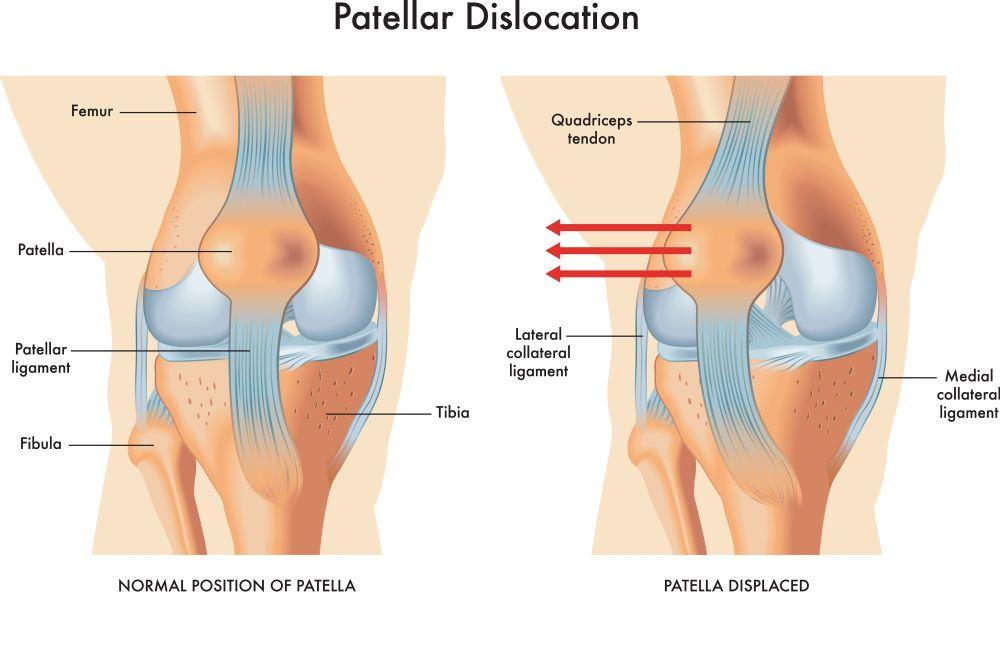
 The patella, also called the kneecap, is the small bone in front of the knee joint where the femur and tibia meet. The patella protects the knee and connects the muscles in front of the thigh to the tibia. When the patella is dislocated, it moves either to the left or to the right of where it is typically located. This injury is different from a dislocated knee which means that the thigh or shin bone is out of place. A dislocated patella can cause significant knee pain and can create a loss of function in the knee.
The patella, also called the kneecap, is the small bone in front of the knee joint where the femur and tibia meet. The patella protects the knee and connects the muscles in front of the thigh to the tibia. When the patella is dislocated, it moves either to the left or to the right of where it is typically located. This injury is different from a dislocated knee which means that the thigh or shin bone is out of place. A dislocated patella can cause significant knee pain and can create a loss of function in the knee.
There are several ways the kneecap or patella can become insecure in its location. Many patella dislocations occur as a result of a sports injury. However, it can be just a sudden twist of minor trauma that can also cause damage. Most first-time patella dislocations occur between the ages of 14 and 18. However, people younger or older can experience this injury as well.
Symptoms of a Dislocated Patella
Symptoms of a dislocated patella can vary depending on how far out of place the patella has moved and how much damage has occurred. General symptoms of a dislocated patella include feeling a “pop” in the knee, swelling, instability, and a change in appearance. Other symptoms include the knee giving way or giving out when pressure is put on it, knee pain when standing or tenderness to the touch, as well as bruising around the knee. Some people say that their kneecap has moved back into place but that it sounds like a rice krispies when used. If someone is experiencing any of these symptoms, they need to seek medical attention right away. Even if the knee cap has moved back into place on its own, you should still seek out the aid of a medical professional. While the patella might look like it is back in the right position, there could be damage to the surrounding muscles or ligaments. If the injury goes untreated, it can result in a lack of function of the knee or permanent damage to the knee.
What To Do Immediately After Injury
 It is essential to seek medical treatment right away after you suspect a dislocated patella. As soon as the injury takes place, the best way to control the swelling is with ice. The knee also needs to be immobilized, but do not try and push the knee back into place. This can cause more damage. Do not put any weight on the injured leg between the injury and seeking medical help. If the injured patient cannot get in to see an orthopedic doctor immediately, call 911 or go to the emergency room.
It is essential to seek medical treatment right away after you suspect a dislocated patella. As soon as the injury takes place, the best way to control the swelling is with ice. The knee also needs to be immobilized, but do not try and push the knee back into place. This can cause more damage. Do not put any weight on the injured leg between the injury and seeking medical help. If the injured patient cannot get in to see an orthopedic doctor immediately, call 911 or go to the emergency room.
Diagnosis
An orthopedic doctor will do a physical examination of the knee as well as ask questions about the injury. Being able to describe how the injury happened as well as how it felt at the time of the injury and afterward call help the doctor with a diagnosis. An x-ray will help determine the damage to the patella and surrounding area. .
Types of Dislocation
There are two types of dislocations: dislocation and subluxation. A dislocated patella occurs when the patella moves out of place and stays out of place. If a patella moves out of place but then quickly and spontaneously moves back into position, it is called a subluxation. Both require medical attention and treatment. If the patella did not go back into place, do not try and push it back into place on your own. This can cause more damage.
Treatment
In order to treat a dislocated patella, an x-ray will be ordered to check the damage done to the patella and the surrounding area. As long as there is no significant damage to the area, the orthopedic doctor will first treat it by moving the kneecap back into place. This is called a reduction. To perform a reduction, the orthopedic doctor will likely give some medication to help relax the muscles around the kneecap and then will apply pressure to the kneecap to get it back into place. Some patients will get light sedation before the procedure. However, if damage has occurred to one of the bones, minor surgery may be needed. Surgery may also be recommended if you have continual dislocations of the patella.
Surgery Options
An initial patella dislocation rarely requires surgery, but if it is a repeated injury or severe damage occurs, surgery may be needed. Some surgical options include arthroscopic surgery, reconstructive surgery, and Tibial tuberosity transfer. Arthroscopic surgery is a minimally invasive procedure with a camera and surgical tools inserted through a small incision in the knee. The surgeon repairs the damage using this noninvasive procedure. Reconstructive surgery is for more severe injuries or when a dislocation has occurred repeatedly. In this surgery, the damaged tendons and ligaments are repaired, and any damaged bone or cartilage is removed. Reconstructive surgery is the most common way to repair a dislocated patella. The tibial tuberosity transfer is the more complex surgery and is usually only done after recurrent patella dislocation. During this surgery, a surgeon will cut a piece of shin bone or tibia and move it to a position that will improve the stability of the patella. Screws are also inserted to keep the bone in place while it heals.
After Dislocation Is Treated
After the patella has been put back into place, ice, anti-inflammatories, and crutches are often used to help keep weight off the patella and reduce the swelling. Just because the kneecap is back in place does not mean the injury is healed. It is very important not to put pressure or weight on the knee while healing. If the knee is overused while it is healing, it can cause more muscle damage. Physical therapy may also be needed after dislocation to strengthen the knee joints and muscles, and some at-home treatments can help you recover more thoroughly.
RICE Method
After the kneecap is back in place, the RICE method is an easy way to remember how to treat the kneecap.
R – Rest the knee to help prevent the injury from getting worse
I – Ice the knee to help reduce inflammation and knee pain
C – Compression can be used by a bandage to ease the swelling as well as provide support to the knee and surrounding muscles and joints
E – Elevate the knee to help reduce the swelling
The RICE method can be used on many injuries, including a dislocation, but it is always best to consult with a doctor. Do not try to treat your injury at home without the consultation of a doctor. Usually, a single dislocated patella will not reoccur; however, it is possible. A repeated dislocation is possible because, after the initial injury, the dislocation often damages the tissue around the knee, and the patella is not as tightly in place – it often remains more unstable than it was before the injury.
Physical Therapy
After being sent home with the dislocation back in place, it is important to periodically rest the knee in an elevated position with ice. You should also use crutches when walking and see a physical therapist to rehab the knee over time. Physical therapy will help use the knee and rebuild the strength within the joints and muscles. It could take between six weeks and three months to fully recover from a dislocated patella. It is very important to finish physical therapy and allow the injury to heal completely. Without the completion of PT, there is a high likelihood of repeated injury. A physical therapist will also provide at-home exercises to keep the knee muscles strong for the long term. After the patella and surrounding muscles have fully healed, most patients can return to their regular lifestyle.
How to Prevent Another Dislocation
Studies have shown that the younger the patient is at the time of the injury, the higher the likelihood of a repeated injury later in life. Some patients also developed arthritis within 20 years of the initial injury. After the patella is dislocated, the ligament and cartilage around the joint are stretched out, which can make it more likely to happen again. Some preventative measures can be taken to help reduce the chances of a similar injury. These include conditioning which helps strengthen all of the muscle groups that keep the knee stable. This will also ensure that no single muscle is working too hard, which could cause a muscle to strain. Stretching also helps ensure that the muscles keep the full range of motion. If another dislocation happens in the same patella, it may require surgery to reset the bone and prevent further injuries.
Avoid Athletic Injury
If the dislocation was related to a sports injury, it is essential to ensure that proper athletic form is being used. If it isn’t, it can put repeated stress on the knee and muscles and cause a secondary injury. A physical therapist, as well as a sports trainer, can help create a plan or routine of exercises to help strengthen the knee to hopefully prevent another injury.
Maximize Nutrients for Healing
Many foods contain healing nutrients that help the bones and muscles regain their full potential. These foods include:
- Dairy products, almonds, broccoli, kale, salmon, and soy products such as tofu – all of these foods are good sources of calcium, which is needed for strong bones.
- Eggs, trout, tuna, and mushrooms are all good sources of Vitamin D, which the body needs to absorb the calcium.
- Tomatoes, olive oil, green leafy vegetables (kale, spinach, collard greens ,and Chinese cabbage), nuts, fatty fish, and fruits (such as oranges, blueberries, cherries, and strawberries) are all good anti-inflammatory foods.
Foods that are considered inflammatory foods and could slow down healing should be avoided:
- Fried Foods
- Sodas
- Refined Carbs
- Lard
- Processed meats
None of these foods provide positive nutrients to the body but will instead increase inflammation and cause the injury to feel worse. They can increase knee pain and slow down healing.
Preventing Arthritis after Injury
Getting arthritis in the knee years after the dislocation is a possibility. However, some things can be done to help prevent arthritis from happening. Managing weight will help keep too much pressure off the knees. Being just 10 pounds overweight can put up to 30 to 60 pounds of additional pressure on the knees when walking. Getting regular exercise will not only help maintain weight but will also strengthen the knee joints and muscles. Getting as many Omega-3’s in the diet as possible will also help prevent arthritis. Omega 3’s can be taken by supplements but can also be found in many foods, including walnuts, flaxseeds, chia seeds, and soybean oil.
Orthopedic Doctors, Physical Therapists, and X-Rays All in One Location
 At AICA Marietta, we have orthopedic doctors who can examine your injury, order an X-ray, and review your treatment options. After your patella dislocation has been corrected, we will get you on the path to recovering fast with one of our many great physical therapists. Don’t let a patella dislocation ruin your lifestyle. Here at AICA Marietta, we want the best possible care for you so that you can get back to doing what you love in life. Call us at AICA Orthopedics to schedule your examination today.
At AICA Marietta, we have orthopedic doctors who can examine your injury, order an X-ray, and review your treatment options. After your patella dislocation has been corrected, we will get you on the path to recovering fast with one of our many great physical therapists. Don’t let a patella dislocation ruin your lifestyle. Here at AICA Marietta, we want the best possible care for you so that you can get back to doing what you love in life. Call us at AICA Orthopedics to schedule your examination today.